
Income tax is an important source of Govt. revenue which is collected from individuals or other entities and utilised on several public welfare channels.
Every citizen who earns above a certain limit is liable to pay the income tax as per the existing tax slabs.
In other words, income tax is nothing but a form of charge imposed by the govt. on the income of its citizens.
Although, it is levied for a collective public benefit in the later stage, people with multiple financial obligations or persons from middle income group like me are more likely to get affected as it reduces the disposable income.
However, govt has a solution to this. In order to minimize the discouraging effect of income tax on our bank balance, govt. has certain provisions that help us save our tax. This is known as ‘tax deduction’ and section 80C is one of the major elements of tax deduction which applies to individuals or Hindu Undivided Families(HUFs).
This article focuses on the meaning and implications of deduction under section 80C of Income Tax Act, 1961. But before let understand what tax deduction means.
What is Tax Deduction?
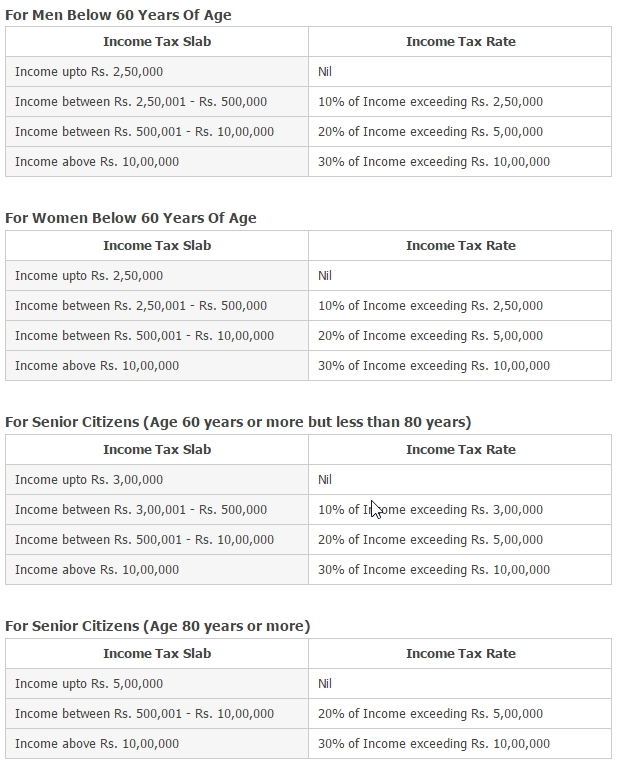
As per the current tax slab for the FY 2016-17, which is same as the previous financial year 2015-16, these are the tax rates based on age group and level of income.
Income tax is unavoidable when your income goes beyond a specific limit. This is your taxable income, which determines the amount of income tax you’re liable to pay in a financial year. Higher the taxable income, higher will be the amount of income tax.
But, with tax deduction, you can reduce your taxable income so that your tax amount will be less. Tax deduction decreases your tax liabilities and saves your tax amount.
The basic objective of tax deduction is to discourage you from hoarding money in bank accounts.
Instead, you can spend or invest your money in certain ways that not only reduce your taxable income for the current financial year but also benefit you in long run. Such activities are eligible for tax deduction and they include investment in insurance schemes, pension fund, or PPF, expenses on education, health matters, and purchase or construction of house. In addition to that, you can also claim tax deduction on charitable contribution such as donation to Prime Minister Relief Fund, religious institutes, local authorities that promote health awareness etc since the govt offers tax exemptions on such spendings. Thus, tax deduction also encourages you to participate in activities that promote social benefits.
Again, depending on the type of tax deduction, your claim amount may vary.
The Income Tax Act of our country is consisting of several sections and subsections. One of them is section 80C which focuses on tax deduction applicable to individuals and HUFs.
Each of the sections and subsections dealing with tax deduction comes with maximum claim amount permissible for a financial year. That is the maximum tax deduction you can claim under a specific section.
Here is what you need to know about the section 80C and its deduction.
What is 80C?
The Income Tax Act, 1961 is the charging statute of income tax till date which amends the law related to income tax and super tax. There are several sections in the Income Tax Act that deal with individual rules and regulation pertaining to income tax in India.
The section 80C of Income Tax Act, 1961 deals with the “deduction in respect of life insurance premia, deferred annuity, contributions to provident fund, subscription to certain equity shares or debentures, etc.” The section typically belongs to the chapter that focuses on the deductions which are to be made while calculating the taxable income
Section 80C is one of the significant components of tax deduction which applies on a number of day to day expenditure carried out by individuals and HUFs.
Here is more about the deductions under section 80C.
Deduction Under Section 80C
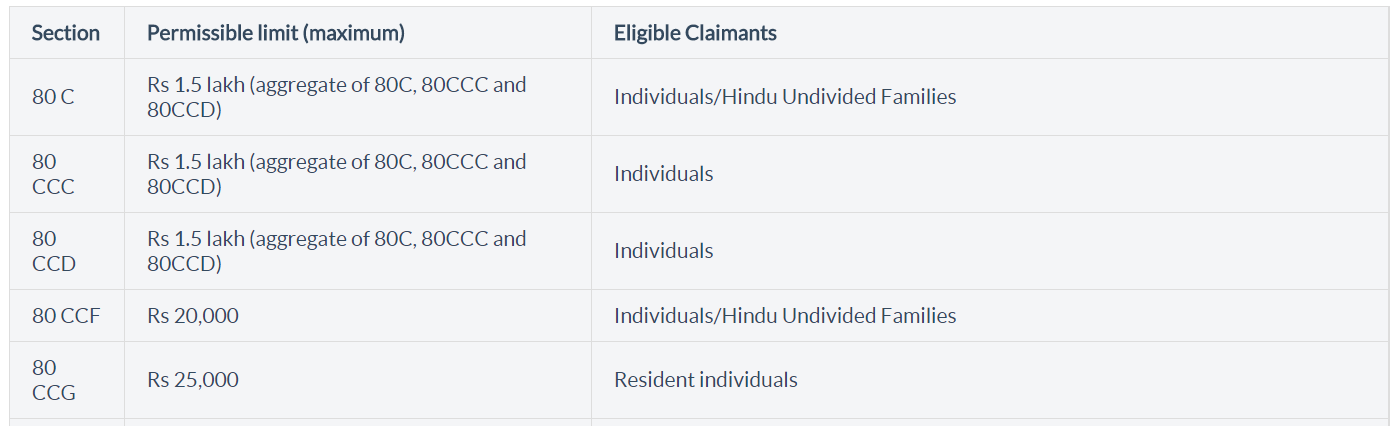
The maximum amount permissible under section 80C deduction for the financial year 2015-16 and Assessment Year 2016-17 is Rs.1.5 lakh.
In other words, you can reduce your total taxable income by Rs.1.5 lakh through section 80C. For this you have to utilise the savings and investment options eligible for tax deduction under 80C.
However, the amount mentioned above is the aggregate of section 80C, 80CCC and 80CCD. That means for all the activities qualifying under these three sections, the maximum amount of tax deduction you can claim will be Rs.1.5 lakh as per the current rules.
Some of the common spending activities under section 80C include,
- Payment of life insurance premium
- Payment made towards pension fund or provident fund
- Expenses on tuition fees
- Fixed deposit with a minimum duration of 5 years
- Construction or purchase of residential property
- Purchasing National Saving Certificates
Section and Subsection-wise Tax Deduction
Section 80C
Covers– Payment made towards life insurance premia, deferred annuity, contributions to provident fund, subscription to certain equity shares or debentures, etc.
Applicable to– Individuals and HUFs
Maximum Limit– Rs.1,50,000
Section 80CCC
Covers- Payment made towards pension fund or Annuity plan of LIC of India
Applicable to– Individual taxpayers
Maximum Limit– Rs.1,50,000
Section 80CCD
Covers- payments made towards pension schemes notified by the govt. Both the employer and employee who contribute towards the pension fund are eligible for tax deduction.
Applicable to- Individual taxpayers
Maximum Limit- 10% employers’ salary
Section 80CCF
Covers– Payment made towards the subscription of long term infrastructure bonds which are notified by the central govt.
Applicable to – Individual taxpayers and HUFs
Maximum Limit– Rs.20,000
Section 80CCG
Covers- Payment made towards investment in Equity savings scheme by resident individuals
Applicable to– Resident individuals
Maximum Limit– 50% of the amount invested in equity savings scheme provided the deduction should not exceed Rs.25,000.
Deduction under section 80C is crucial because it has a positive effect on the individual taxpayers. It covers many popular investment options available in India such as National Saving Certificates, Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana, PPF, ELSS, Tax saving Fixed Deposit scheme, ULIPs and many more. Important is to know exactly where and how much you have to invest so that you can make the best use of section 80C and its subsections.
Recommended reading: Guide to Section 80 Deductions
Leave a Reply